-
- Redirect to a Menu Item After Form Submission
- Tracking Form Lead Source
- Show a Form Only to Logged-In Users
- How to Increment a Count on Each Form Submission
- Adding an “Other” Option
- Adding a Unique ID to Each Form Submission
- Show or Hide Form Fields Based on User Joomla User Group
- Disabling Browser Autocomplete for Form Fields
- Scroll the Page to the Top When a Long Form is Submitted
- Display Submissions Count for a Specific Form
- Populate Drop Down, Radio Buttons or Checkboxes with a CSV File
- Automatically Delete Submissions Older Than X Days
- Silently POST Submitted Data to Any API or URL
- Automatically Save Each Submission to a JSON file
- Create a Custom Login Form
- Auto-Populate Fields with Article Data
- Add a placeholder text to a Dropdown field
- Create Multilingual Forms in Joomla
- Redirect User to a URL After Form Submission
- Importing and Exporting Forms
- Exporting Form Submissions
- Display Convert Forms in a popup
-
- How to Create a Quiz Form
- Show Confirmation Popup After Submission
- Using the Conditional Content Shortcode in Convert Forms
- Copy Value From One Field to Another
- Submission Tasks
- Exporting Form Submissions with a Webhook URL
- Conditional Fields
- PDF Generator
- Input Masking
- Calculations
- Populate Fields Using Query String
- Smart Tags
-
- Minimum Time to Submit
- Restrict Form Submissions Based on IP
- Enforcing a Custom Password Policy in Convert Forms
- Add Cloudflare Turnstile to your Joomla Form
- Implement the Iubenda Consent Database in Joomla with Convert Forms
- Add Custom Validations to Fields and Forms
- Add Math Captcha to your Form
- Prevent a Field From Saving in the Database
- Add hCaptcha to your Form
- Enable Double Opt-in
- Allow Form Submissions in Specific Date Range
- Ensure a Unique Value is Entered Into a Field
- Block Form Submissions Containing Profanity (Bad Words)
- Block Email Addresses or Email Domains
- Honeypot
- Setting Up Google reCAPTCHA
- Create GDPR Compliant Forms
Calculations
Create online calculation forms that perform real-time calculations. Automate complex calculations, simplify payments and scoring.

Are you wondering how you can calculate a total based on the option selected by the user from your form? With the Convert Forms Calculations Feature, you can create forms with dynamically calculated fields to display the calculated values.
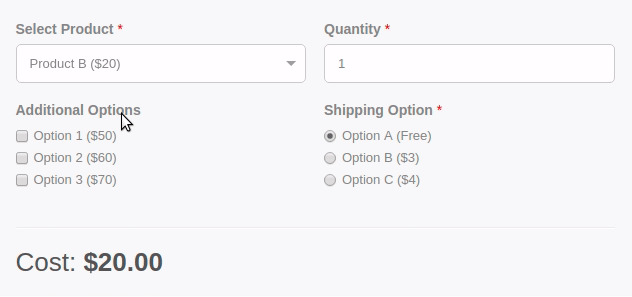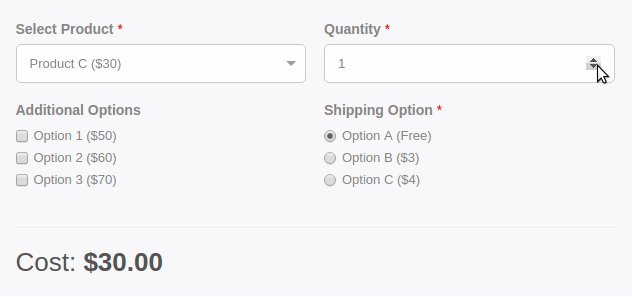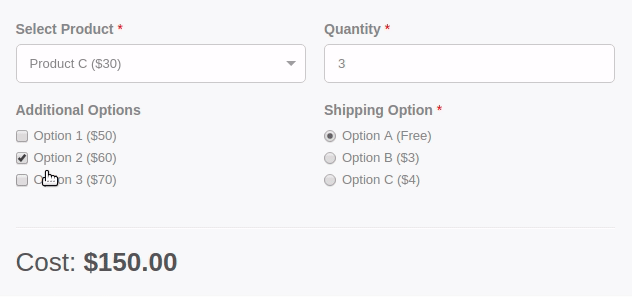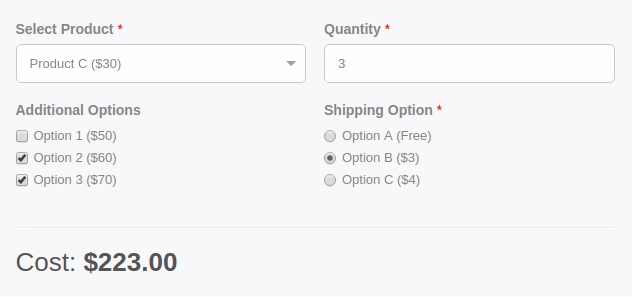
It includes a Visual Calculation Builder that can help you create both single and complex calculations, such as general calculators, ideal weight calculators, calorie calculators, estimate quotes for hotel booking and rent-a-car services, price estimation quotes for appointments and services, loan and finance calculators, and many more.
Features
Here's what makes the Convert Forms Calculations feature a powerful tool for your forms.
- Easy and visual calculator interface.
- Use hidden fields, text fields, number, drop-down, checkbox or radio buttons.
- Supports math operators like +, -, * or /.
- Supports advanced math functions.
- Use conditional logic in calculations.
- Manage multiple calculations in a form.
- Hide calculated fields.
- Use nested calculations.
- Add a prefix or suffix to the calculated value.
- Store calculations in the database.
- Send calculated values via e-mail.
- Create custom calculations with your formula.
How to create a Calculation
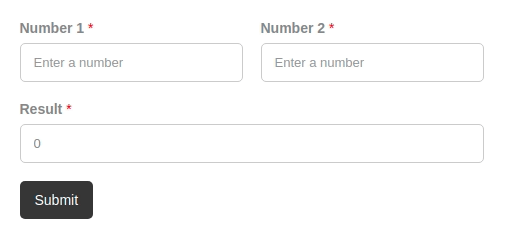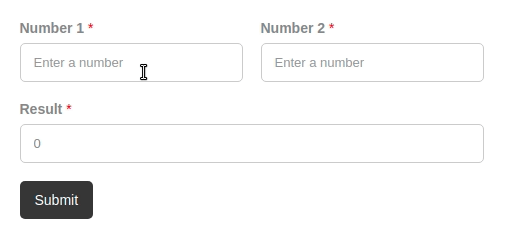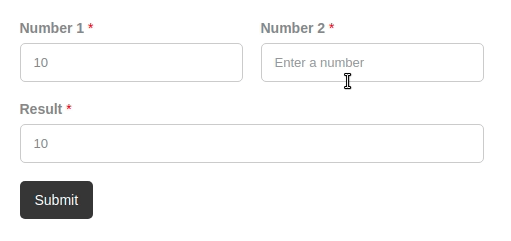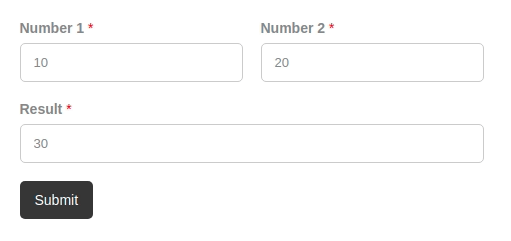
Let's see how you can easily create a form calculation that displays the sum of 2 fields in a third field, as shown in the picture below.
Step 1: Create the form
In order to create a calculation, we need a form with fields, of course! In our example, we are going to use just three Text or Number fields and a submit button. Let's call the first field number 1, the second field number 2, and the third one for the calculated value, result.
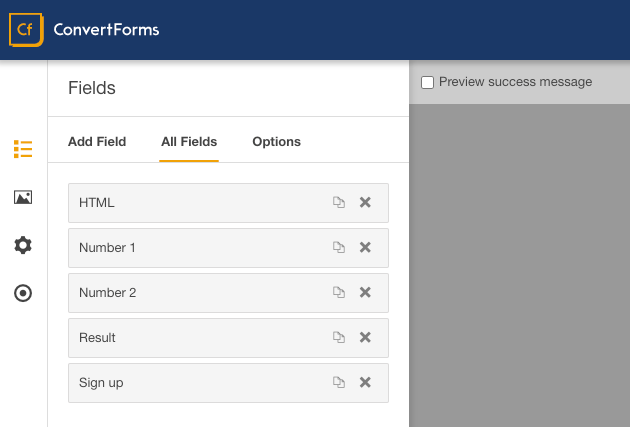
Step 2: Enable Calculations option on the 3rd field
Once the form is ready and the fields are added, click on the 3rd field (where we want to display the calculated value), to open the field settings on the left. Please scroll down to find the Calculations section and click to enable it.
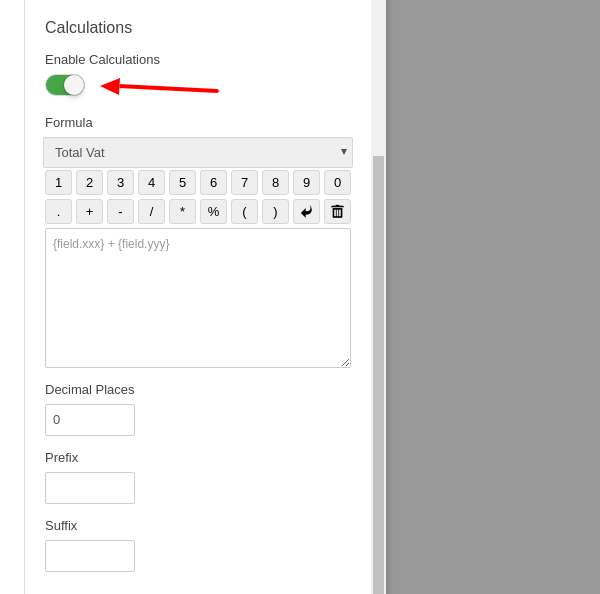
Step 3: Create the Calculation Formula
Although our formula is rather simple, we will use the Calculation Visual Builder to create it. The steps are shown in the animated movie but also described in the bullets below:
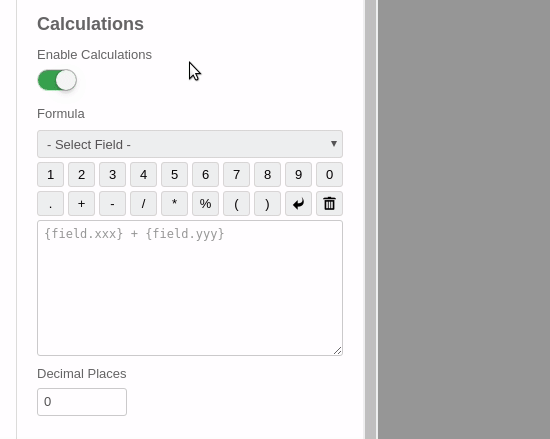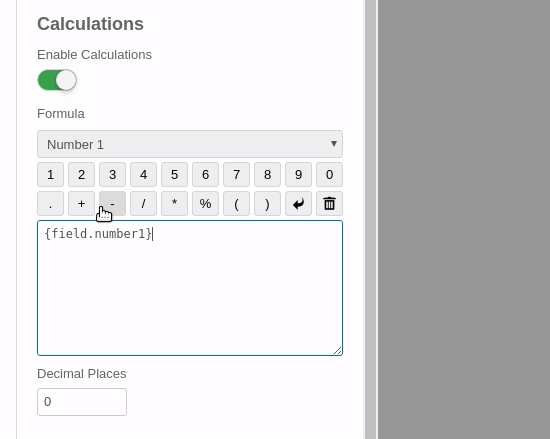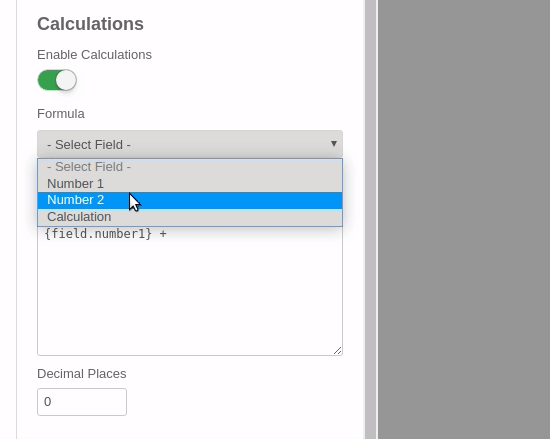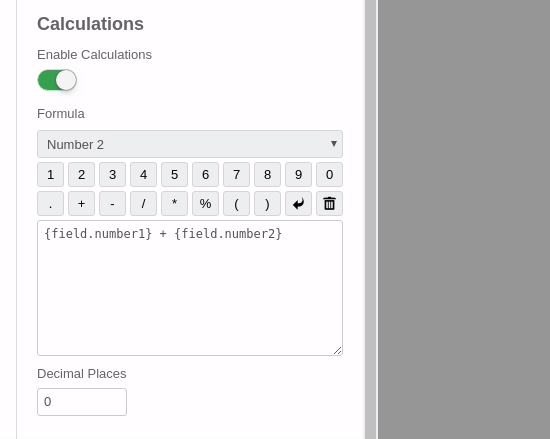
- Click on the Field selection dropdown and add the 1st field.
- From the toolbar, click to add the '+' math operator to our formula.
- Click on the Field selection dropdown again and add the 2nd field.
- Set the Decimal Places option to 0.
- Optionally, you can set a Prefix and Suffix to your calculation field. Note: The field that will be used must support characters, such as a Text Field. If you use a Number Field, you won't be able to see the prefix/suffix as it only supports numbers.
Done! Save your form and test it on the front end.
Assign Calculation Values to Dropdowns, Radio Buttons and Checkboxes
Calculation Values are generally used for calculations and represent an input field's numerical value. The Calculation Value of a field is different from its Value. A field's Value is what is passed into the final form submission. The Calculation Value is used when that field is used in a calculation. This feature is only available in the following fields:
- Dropdown Field
- Multiple Choice Field (Radio)
- Checkboxes Field
How to assign Calculcation Values
Select the field to assign calculation values on these fields and click to open its field settings on the left screen. Scroll to the Choices section and toggle the Use Calculation Values option to ON.
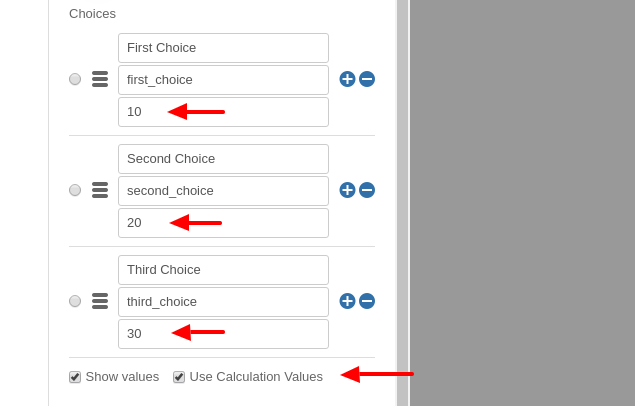
Once the Use Calculation Values option is turned ON, a third input box appears where you can type in the respective calculation value for each option.
Using the screenshot above as a template, if the user selected both “First Choice” and “Second Choice” on the front end, the saved form data would read “first_choice” and “second_choice” respectively. The Calculation Value for the field would be 30 (10 + 20, the sum of the two choice's calculation values).
Formula Syntax
Operator Precedence
The parser accepts a pretty basic grammar. It's similar to normal JavaScript expressions but is more math-oriented. For example, the ^ operator is exponentiation, not xor.
| Operator | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| + | Add | x + y |
| + | Unary plus | +y |
| - | Subtract | x - y |
| - | Unary minus | -y |
| / | Divide | x / y |
| * | Multiply | x * y |
| % | Remainder | x % y |
| = | Assignment | x = y |
| == | Equal | x == y |
| != | Unequal | x != y |
| >= | Greater than or equal | x >= y |
| <= | Less than or equal | x <= y |
| > | Greater than | x > y |
| < | Less than | x < y |
| (...) | Grouping | (x) |
| ! | Factorial | y! |
| ^ | Power | x ^ y |
| and | Logical AND | x and y |
| or | Logical OR | x or y |
| ? : | Conditional statements (If-Then-Else) | x ? y : z |
Unary operators
The parser has several built-in "functions" that are unary operators. The primary difference between these and functions is that they can only accept exactly one argument, and parentheses are optional. With parentheses, they have the same precedence as function calls, but without parentheses, they keep their normal precedence (just below ^). For example, sin(x)^2 is equivalent to (sin x)^2, and sin x^2 is equivalent to sin(x^2).
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| abs x | Absolute value (magnatude) of x. |
| acos x | Arc cosine of x. |
| acosh x | Hyperbolic arc cosine of x. |
| asin x | Arc sine of x. |
| asinh x | Hyperbolic arc sine of x. |
| atan x | Arc tangent of x. |
| atanh x | Hyperbolic arc tangent of x. |
| ceil x | Ceiling of x — the smallest integer that’s >= x. |
| cos x | Cosine of x. |
| cosh x | Hyperbolic cosine of x. |
| exp x | e^x (exponential/antilogarithm function with base e). |
| floor x | Floor of x — the largest integer that’s <= x. |
| length x | String length of x. |
| ln x | Natural logarithm of x. |
| log x | Natural logarithm of x (synonym for ln, not base-10). |
| log10 x | Base-10 logarithm of x. |
| not x | Logical NOT operator. |
| round x | X, rounded to the nearest integer, using "gradeschool rounding". |
| sin x | Sine of x. |
| sinh x | Hyperbolic sine of x. |
| sqrt x | Square root of x. Result is NaN (Not a Number) if x is negative. |
| tan x | Tangent of x. |
| tanh x | Hyperbolic tangent of x. |
| trunc x | Integral part of a X, looks like floor(x) unless for negative number. |
Pre-defined functions
Besides the "operator" functions, there are several pre-defined functions.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| random(n) | Get a random number in the range [0, n). If n is zero, or not provided, it defaults to 1. |
| min(a,b,…) | Get the smallest (minimum) number in the list. |
| max(a,b,…) | Get the largest (maximum) number in the list. |
| hypot(a,b) | Hypotenuse, i.e. the square root of the sum of squares of its arguments. |
| pyt(a, b) | Alias for hypot. |
| pow(x, y) | Equivalent to x^y. For consistency with JavaScript's Math object. |
| atan2(y, x) | Arc tangent of x/y. i.e. the angle between (0, 0) and (x, y) in radians. |
| if(c, a, b) | Function form of c ? a : b |
| roundTo(x, n) | Rounds x to n places after the decimal point. |
Constants
There's also a number of pre-defined constants that can be used in calculations. These are shown in the table below:
| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| E | The value of E represents the base of natural logarithms, e, approximately 2.718. |
| PI | The value of PI represents the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, approximately 3.14. |
| true | Logical true value |
| false | Logical false value |
How to display a Calculation in a HTML Field
Besides that you can display the result of a calculation in an input field, you can also display the evaluated result of a calculation in any HTML element like a <span>, <p>or a <div> tag. Let's see how this is possible.
Add an HTML field from the Fields section to your form. Once added, open the HTML field settings and see the Default Value option with the rich text editor. Click the source code button in the editor's toolbar to open the Source Code dialog. Here, we must add an HTML element with specific HTML data attributes to act as a placeholder for the calculation result.
Using the example described in the How to Create a Calculation section, let's say we also want to display the sum of the two fields in an element. To make that happen, we will need to add the following HTML code:
Sum: <span data-calc="{field.number1} + {field.number2}">0</span>In the code above, we define the same formula we've used in the hidden field using the data-calc attribute while setting the default text to 0. When a value of any of our form fields changes, the calculation will run again, and the result will be displayed within our HTML element.
Using the Calculated Value from another field
Although our calculation works, it's not that efficient. The sum of the two fields is already calculated in the Hidden field since it's ordered before the HTML field. Wouldn't it be better to pull the already computed value from the Hidden field and display it in our HTML element instead of running the same calculation repeatedly? For the sake of simplicity, our code can be rewritten as:
Sum: <span data-calc="{field.result}">0</span>In the updated code, we set the calculation formula to match the value of the result field, which will already have the calculated value when the calculations are triggered since the calculations are executed from top to bottom. The behavior of using the estimated value of another field in a calculation is known as Calculation Nesting.
Supported HTML Attributes
Below is a list of the HTML attributes you can use to customize an inline calculation.
| Property Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| data-calc | The formula syntax | Text |
| data-precision | Define the decimal places' precision | Number |
| data-prefix | Add text at the beginning of the calculated value | Text |
| data-suffix | Add text at the end of the calculated value | Text |
| data-thousand_separator | Make big numbers more readable by separating thousands with a comma. | Text |
| data-decimal_separator | Make big numbers more readable by separating decimals with a dot. | Text |
Frequently Asked Questions
How to use data from the database in a calculation?
To include database information in a calculation, you'll need to add a Hidden field to the form and pre-populate its value using PHP during the Form Prepare event. See the PHP Scripts guide to learn how to make that happen. Then, you can use your hidden field in the calculation.
How to use a query string parameter in a calculation?
To use a query string parameter in a calculation, first add a Hidden field to the form and set its value with the Query String Smart Tag {querystring.PARAM} and then use that hidden field in the calculation.
When are the calculations processed?
Calculations are processed in the browser during page load and every time a field value changes. This ensures the results are updated live, providing a great user experience. For security reasons, the calculations are re-run during submission to prevent tampering and illegal field manipulation.
In which order are the formulas associated with calculated fields?
Each time a field value changes, an event is fired to re-calculate all the fields from top to bottom so that every value is added consecutively.
- Product A: 15 | Price = 15
- Product B: 20 | Price = 35
- Product C: 10 | Price = 45
- Price = 45
How do you use conditional statements in a calculation?
Let's say you have created a form to sell a book and I'd like to give a special 30% discount when the quantity is three or more. There are two ways to do so:
1. Using the ternary operator (x ? y : z)
{field.qty} >= 3 ? 30 : 02. Using the if built-in method if(condition, value if true, value if false) which accepts 3 arguments.
if({field.qty} >= 3, 30, 0)Can I perform calculations with dates?
Unfortunately, this is not supported yet. It's on our to-do list, but there's no ETA on when this feature will be available. Until then, you can use a workaround with a small JavaScript snippet that can help you calculate the difference between 2 date fields.
Javascript workaround for calculating the difference between 2 dates
- Add 2 Date / Time fields to your form and add the classes fp_check_in and fp_check_out to the CSS Class setting.
- Add a Hidden Field to your form and set the field's name to number_of_days. This will store the days between the two dates and can be use in your calculations.
- Place the following JavaScript code in your form's "Custom JavaScript" section, which can be found under the Design -> Advanced panel.
ConvertForms.Helper.onReady(() => {
setTimeout(function () {
const checkin = document.querySelector(".fp_check_in input.flatpickr-input")._flatpickr;
const checkout = document.querySelector(".fp_check_out input.flatpickr-input")._flatpickr;
checkin.set('disableMobile', true);
checkin.set('onClose', (date) => {
if (date != '' && checkout.selectedDates != '') {
calculateDays(date, checkout.selectedDates);
}
});
checkout.set('disableMobile', true);
checkout.set('onClose', (date) => {
if (checkin.selectedDates != '' && date != '') {
calculateDays(checkin.selectedDates, date);
}
});
function calculateDays(check_in, check_out) {
const date1 = new Date(check_in);
const date2 = new Date(check_out);
// To calculate the time difference of two dates
let Difference_In_Time = date2.getTime() - date1.getTime();
// To calculate the no. of days between two dates
let Difference_In_Days = Math.ceil(Difference_In_Time / (1000 * 3600 * 24));
if (Difference_In_Days < 0) {
Difference_In_Days = 0;
}
const el = document.querySelector('input[name="cf[number_of_days]"]');
el.value = Difference_In_Days;
el.dispatchEvent(new Event('input', { 'bubbles': true }));
el.dispatchEvent(new Event('change', { 'bubbles': true }));
}
}, 500);
});After finishing the above guide, you can use the hidden field num_of_days in your Field Calculations.
Why does the field contain a previous value other than the currently calculated one?
If you use JavaScript to populate a hidden field, which you then use in another field's calculation, you may find that the latter does not update its value and displays the previous value of the hidden field. This is because the calculations do not run after you update the hidden field. You will need to trigger the calculations right after you change the hidden field's value.
Below, you can find how to trigger the calculations to re-run when you update a field:
var el = document.querySelector("#input");
el.value = 70;
el.dispatchEvent(new Event('input', { 'bubbles': true }));You can also trigger the calculations on the form itself:
var el = document.querySelector("#input");
el.value = 70;
el.closest("form").dispatchEvent(new Event('input'));Troubleshooting
Chrome doesn't display my calculation result inside a Number Field.
At the moment, due to the way that Chrome handles the formatting of numbers, you cannot assign the calculation's result to a Number Field while using the comma (,) Decimal Separator. As a workaround you can switch to a Textbox Field or use the dot (.) Decimal Separator.
- Features
- How to create a Calculation
- Assign Calculation Values to Dropdowns, Radio Buttons and Checkboxes
- Formula Syntax
- How to display a Calculation in a HTML Field
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How to use data from the database in a calculation?
- How to use a query string parameter in a calculation?
- When are the calculations processed?
- In which order are the formulas associated with calculated fields?
- How do you use conditional statements in a calculation?
- Can I perform calculations with dates?
- Why does the field contain a previous value other than the currently calculated one?
- Troubleshooting







 Rated:
Rated: 